
Jun
For the first time in history, the RBI’s foreign exchange (forex) reserves have increased to more than USD 500 billion. For the week ending June 5, 2020, RBI’s forex reserves increased by USD 8.4 billion. Since April 3, 2020, forex reserves have increased by approximately USD 27 billion.
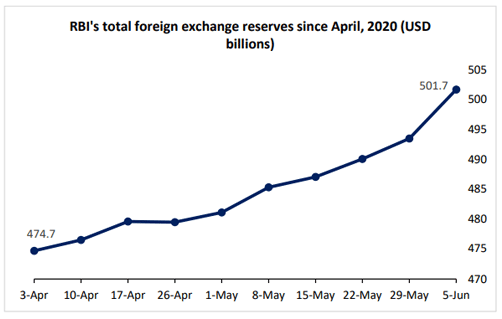
Why have forex reserves increased?
The most likely reason for the rise in forex reserves is the rise in investments by Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) and Foreign Direct Investments (FDI). Foreign investors have bought stakes in several Indian companies in the last two months, which include mega block deals in Reliance Group’s subsidiary Jio Platforms, Kotak Mahindra Bank and Bharti Airtel. In the first 15 days of June 2020, FPIs have bought in approximately Rs. 20,621 crore in Indian debt and equity markets.
Additionally, the narrowing current account deficit due to Covid-19 imposed restrictions is also believed to be a major factor behind increasing forex reserves. The fall in oil prices have significantly reduced our import bill, which saves a lot of forex reserves. The depreciation of the USD against other major currencies like Euro, Pounds and Yen, would have also resulted in revaluation gains.
How do rising forex reserves help us?
Large forex reserves play a significant role by making it easier for the Indian Government and the RBI to manage India’s external and internal financial issues. This is even more important at a time when the economy is impacted by Covid-19 induced slowdown. Currently, our forex reserves are enough to cover the import bill of more than one year. This is a big cushion to help the country from an economic standpoint. Analysts believe that the RBI has been increasing its reserves to guard against a possible downgrade of India’s credit rating by international rating agencies and protect against possible risk-off sentiments. The RBI can also use the reserves in managing and maintaining the stability of the Indian Rupee.
Large forex reserves is believed to provide the market some confidence of the ability of the country to meet its external liabilities. It also helps the RBI to assist the government in its foreign exchange needs and maintain a reserve for national disasters or emergencies.
Sources: RBI, NSDL and publicly available information
Disclaimer: The information provided herein is based on publicly available information and other sources
believed to be reliable, but involve uncertainties that could cause actual events to differ materially from
those expressed or implied in such statements.

